Troubleshooting for Fat Client
If your deviceTRUST deployment is not working within your local devices, then these simple troubleshooting steps will ensure your environment is up and running as expected.
We will perform the following steps:
- Step 1: Make sure that you have a valid license
- Step 2: Check that your contextual security policy has been saved and deployed
- Step 3: Check that the user is managed by deviceTRUST
- Step 4: Check that your contexts are correctly defined
- Step 5: Exclude specific users from the deviceTRUST policy
- Step 6: Check that the deviceTRUST Host service is running
- Step 7: Check that you are using the latest deviceTRUST version
- Step 8: Open a support ticket with us
Step 1: Make sure that you have a valid license
If your deviceTRUST License has not been configured, or has expired, then you may find that the deviceTRUST functionality is disabled.
To check if licensing is causing a problem, open the Windows Event Log on the local device and navigate to APPLICATION AND SERVICE LOGS\DEVICETRUST\ADMIN and look for an Event ID between 11 and 16.
- Event ID 11 is used to report a valid license.
- Event ID 12 and 13 are used to report a license that will soon expire.
- Event ID 14, 15 and 16 are used to report an invalid license.
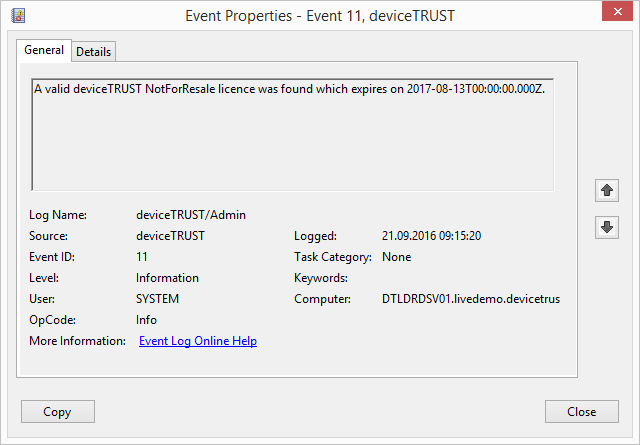
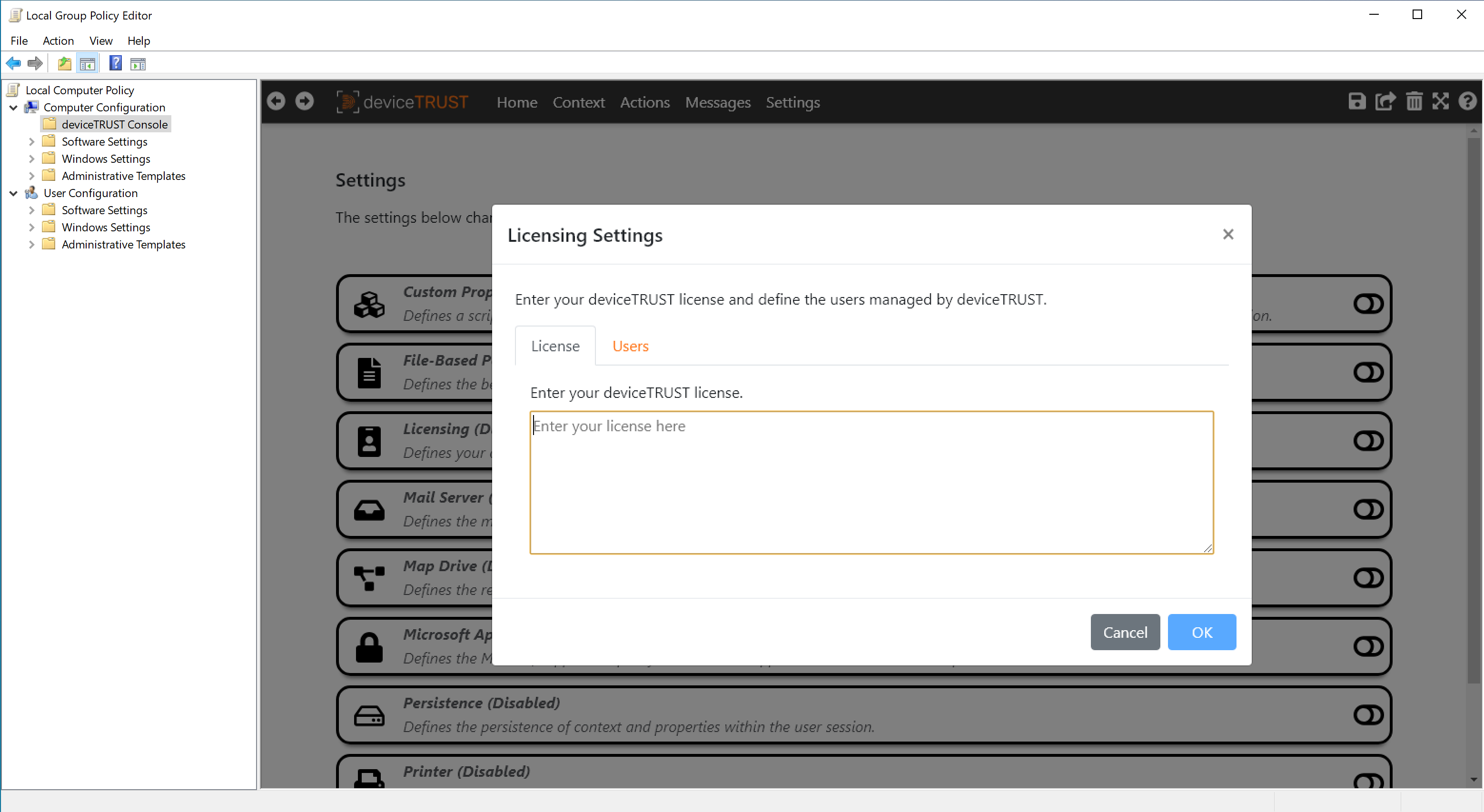
If your Windows Event Log reports a licensing event other that Event ID 11, then you should check your license. Within the deviceTRUST Console, open your policy and navigate to DEVICETRUST CONSOLE and then click on the SETTINGS tab. Select LICENSING and verify that your deviceTRUST license has been correctly entered. If a wrong or incorrect license was entered, correct the license, click OK and then save your active deviceTRUST contextual security policy before updating it on the remoting host.
Step 2: Check that your contextual security policy has been saved and deployed
Ensure that your deviceTRUST contextual security policy has been saved within the deviceTRUST Console and successfully deployed to the local devices.
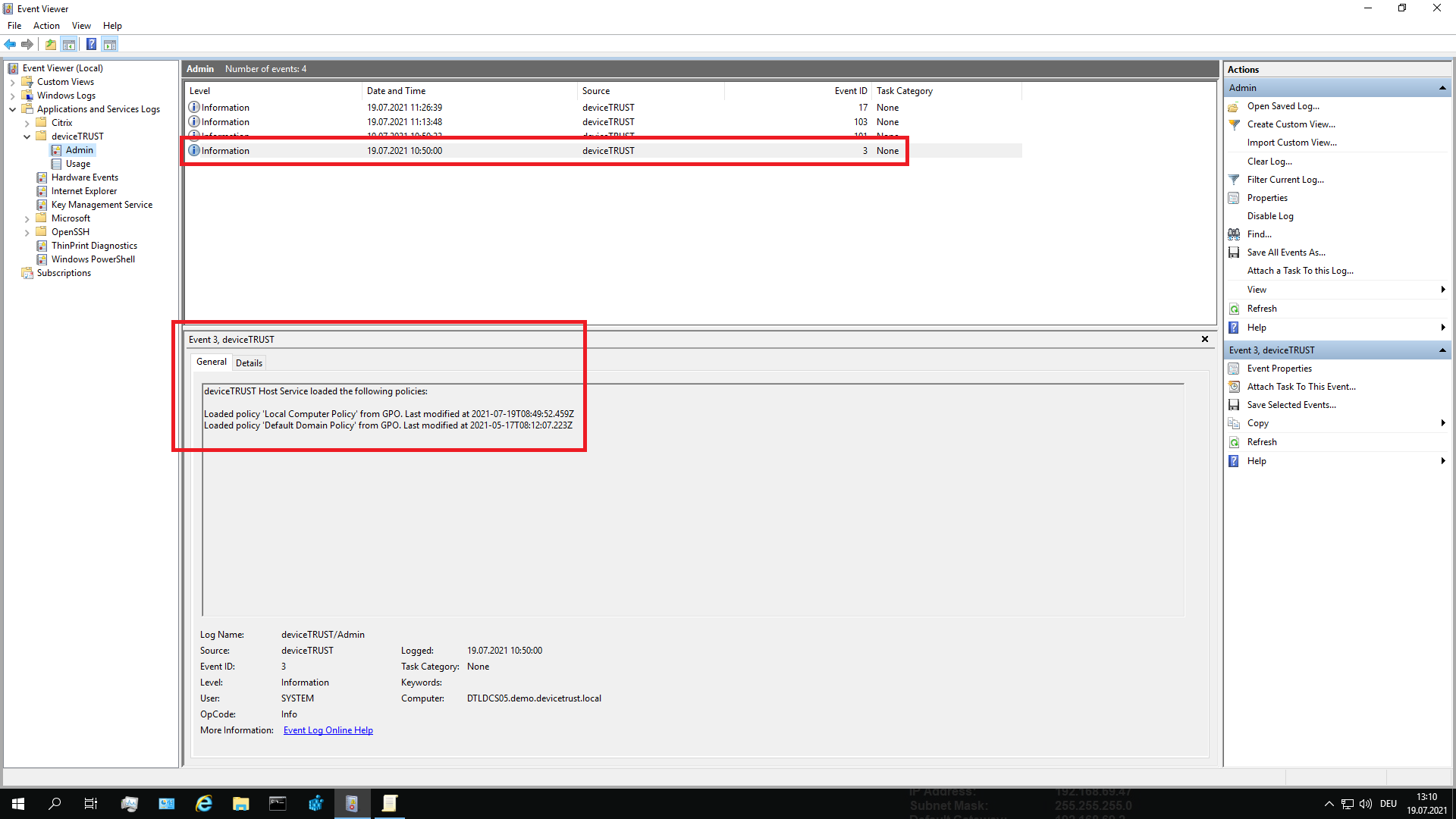
To check which policies are effective, open the Windows Event Log on the local device and navigate to APPLICATION AND SERVICE LOGS\DEVICETRUST\ADMIN and look for Event ID 3 which details the name of each policy and the timestamp that it was last modified.
- User sessions get their deviceTRUST policies during login and are active until the session is logged out. If newer contextual security policies are deployed on the local device during this time, they will not affect running user sessions, only new logins.
If the policy is not listed or does not have the expected timestamp, then firstly make sure that you have successfully saved the policy from within the deviceTRUST Console.
Next, the policy must be successfully deployed to the local device. The method used to deploy the policy depends upon the where the policy changes were saved.
Local Policy
When using local policy, no additional steps need to be taken to enable the updated contextual security policy for the deviceTRUST Host.
Group Policy Object (GPO)
When using group policy, a Group Policy update should be forced on the local device to propagate an update of the contextual security policy. Of course, it is also possible to wait for the next group policy refresh, but for testing purposes this can be forced directly with a call to GPUPDATE /TARGET:COMPUTER /FORCE. After the updated contextual security policy is successfully deployed to the local device, the deviceTRUST Host will use it immediately.
File-based
When using file-based policy, the updated contextual security policy is copied to the appropriate target directory as a file-based policy on the local device. After the updated file-based contextual security policy is copied to the target directory, the deviceTRUST Host will use it immediately.
Step 3: Check that the user is managed by deviceTRUST
The deviceTRUST contextual security policy defines the users that will be managed by deviceTRUST. By default, this does not include members of the local administrators group.
To check if an unmanaged user has signed in, open the Windows Event Log on the local device and navigate to APPLICATION AND SERVICE LOGS\DEVICETRUST\ADMIN and look for Event ID 17.
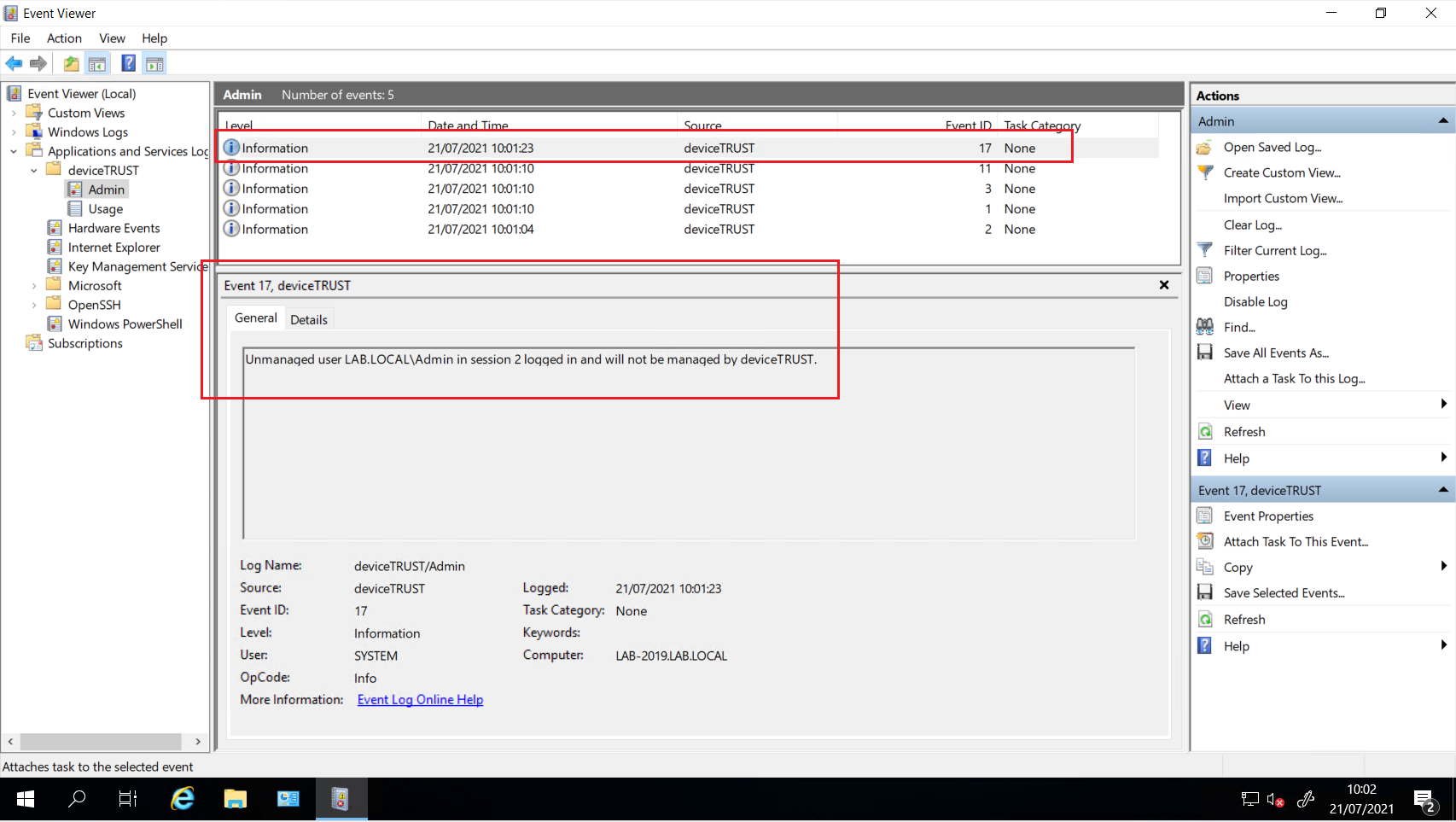
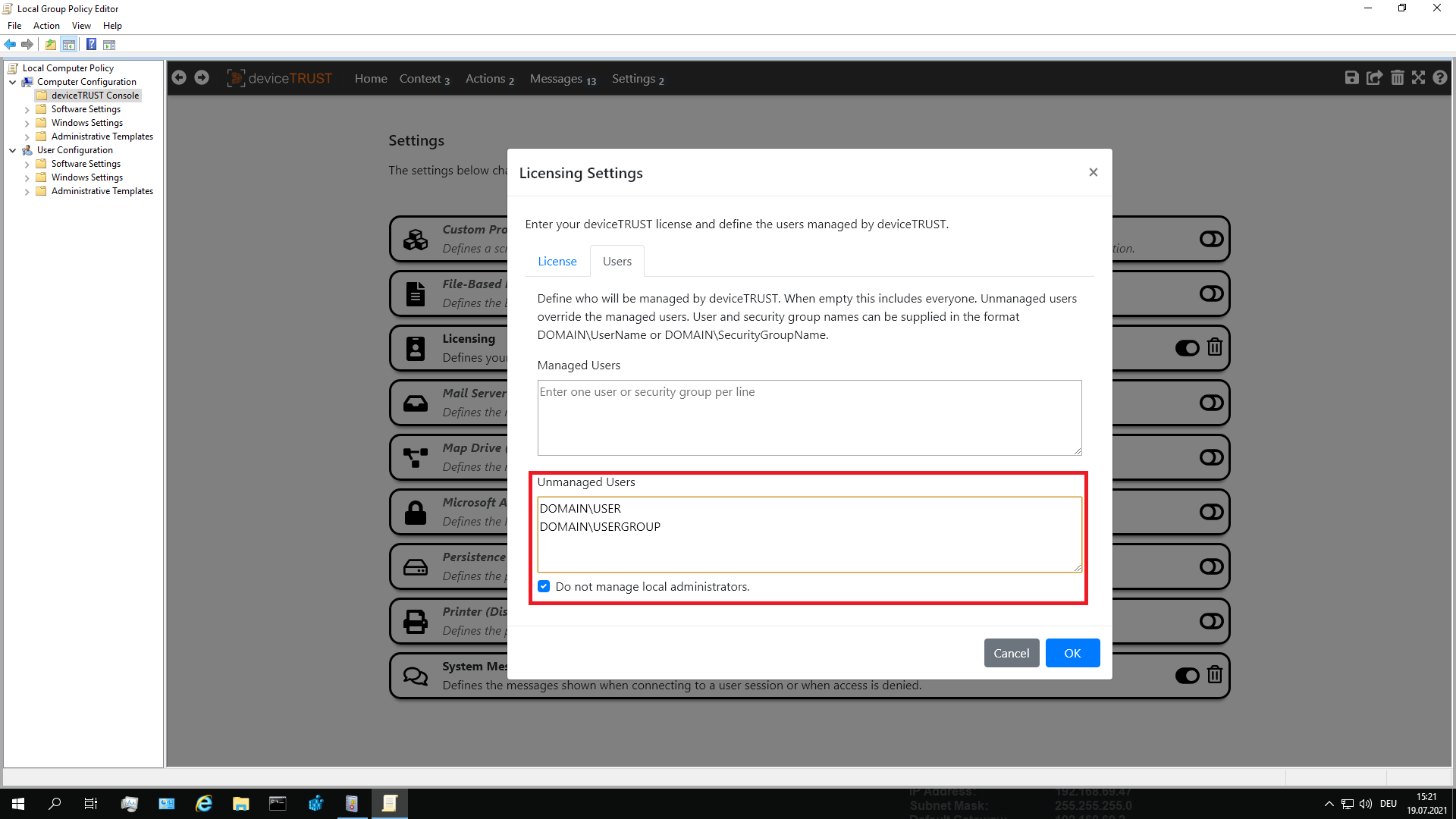
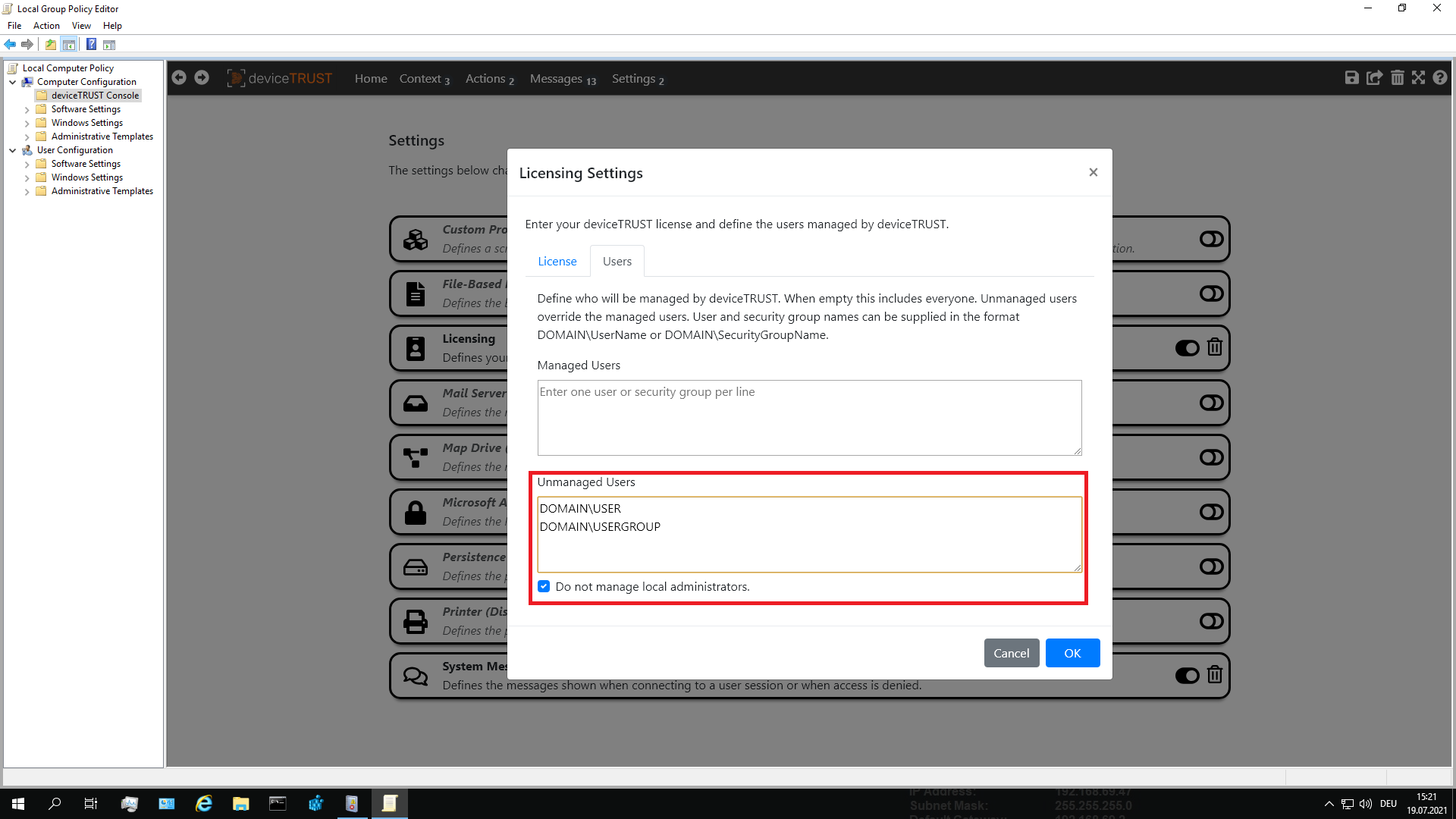
To change the list of managed users, open your active deviceTRUST contextual security policy and navigate to DEVICETRUST CONSOLE and click on the SETTINGS tab. Select LICENSING, navigate to the USERS tab and check that the user account is not configured in the UNMANAGED USERS directly or via a group membership.
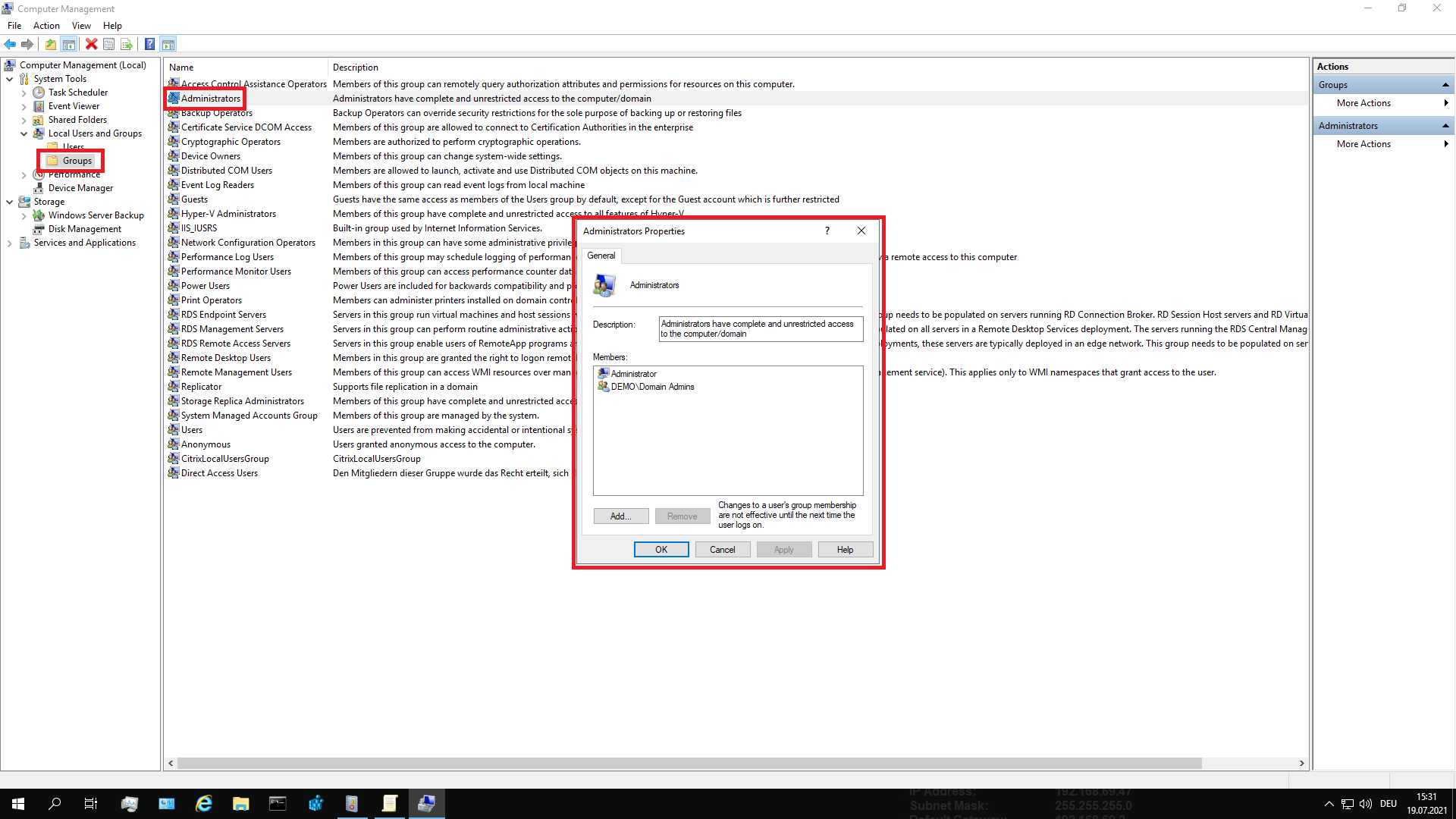
If deviceTRUST policies are still not applied to the user, check if the user account is a member of the local administrators group. To do this, start COMPUTER MANAGEMENT on the local device, navigate to SYSTEM TOOLS, select LOCAL USERS AND GROUPS and check that the user is not a member of the ADMINISTRATORS group.
Step 4: Check that your contexts are correctly defined
The deviceTRUST Console is used to create and configure the contexts on which targeted actions are then defined. Therefore it is very important that the contexts and their logical status is correctly defined. Inaccuracies in the logic can have an undesirable impact on the user. To analyze what exactly led to the undesired action, it is necessary to check the status of the respective context for its correctness.
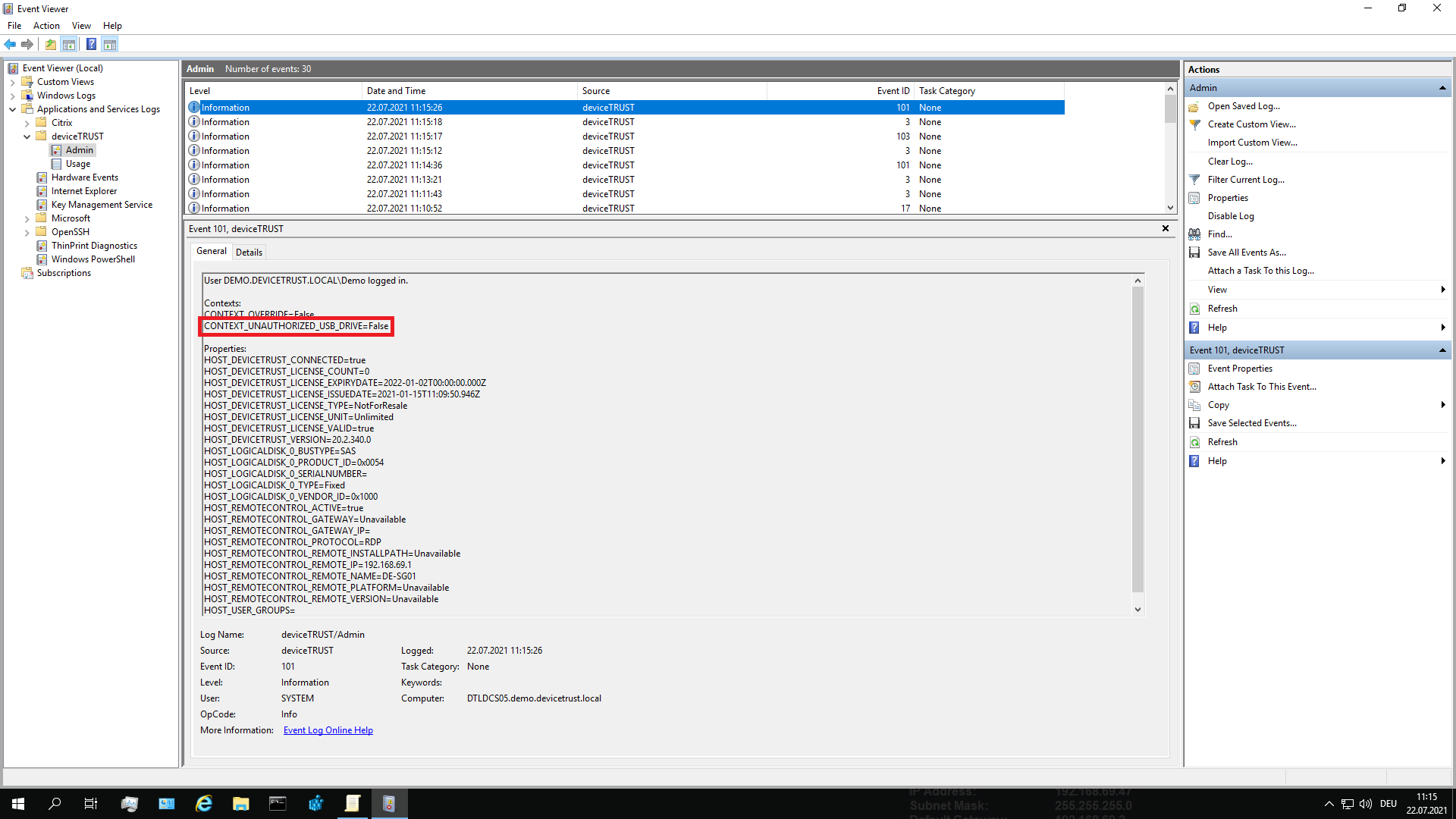
In the following example, the context UNAUTHORIZED USB DRIVE was defined, which gives an indication whether the USB drive used was authorized for use on the local device. Based on the logical configuration of the context UNAUTHORIZED USB DRIVE, the status values FALSE and TRUE are possible.
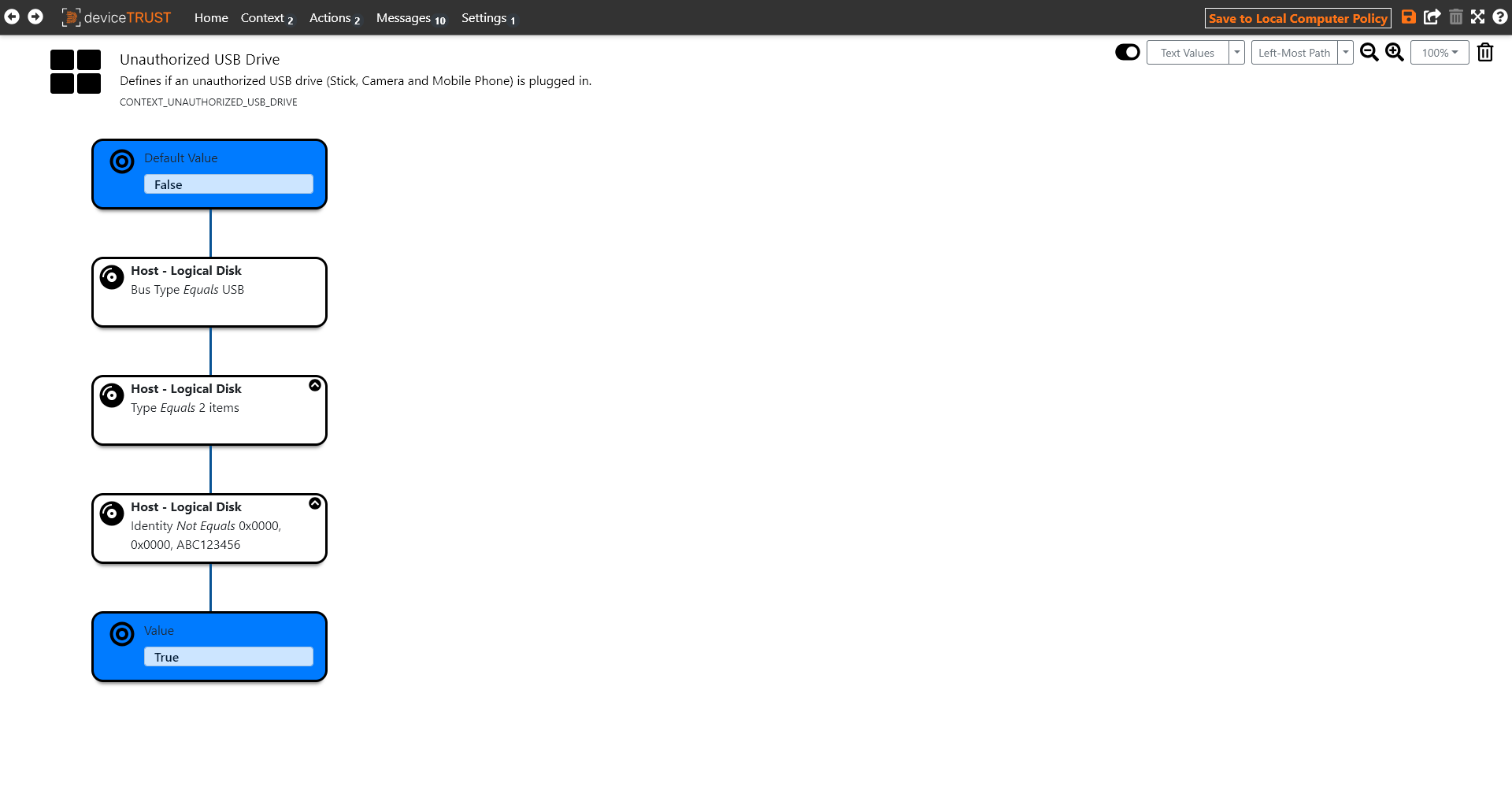
The context value that has been evaluated for a user session can be seen by opening the Windows Event Log on the local device and navigating to APPLICATION AND SERVICE LOGS\DEVICETRUST\ADMIN. Event ID 101 is raised during logon, and details the properties and context of the users’ local session.
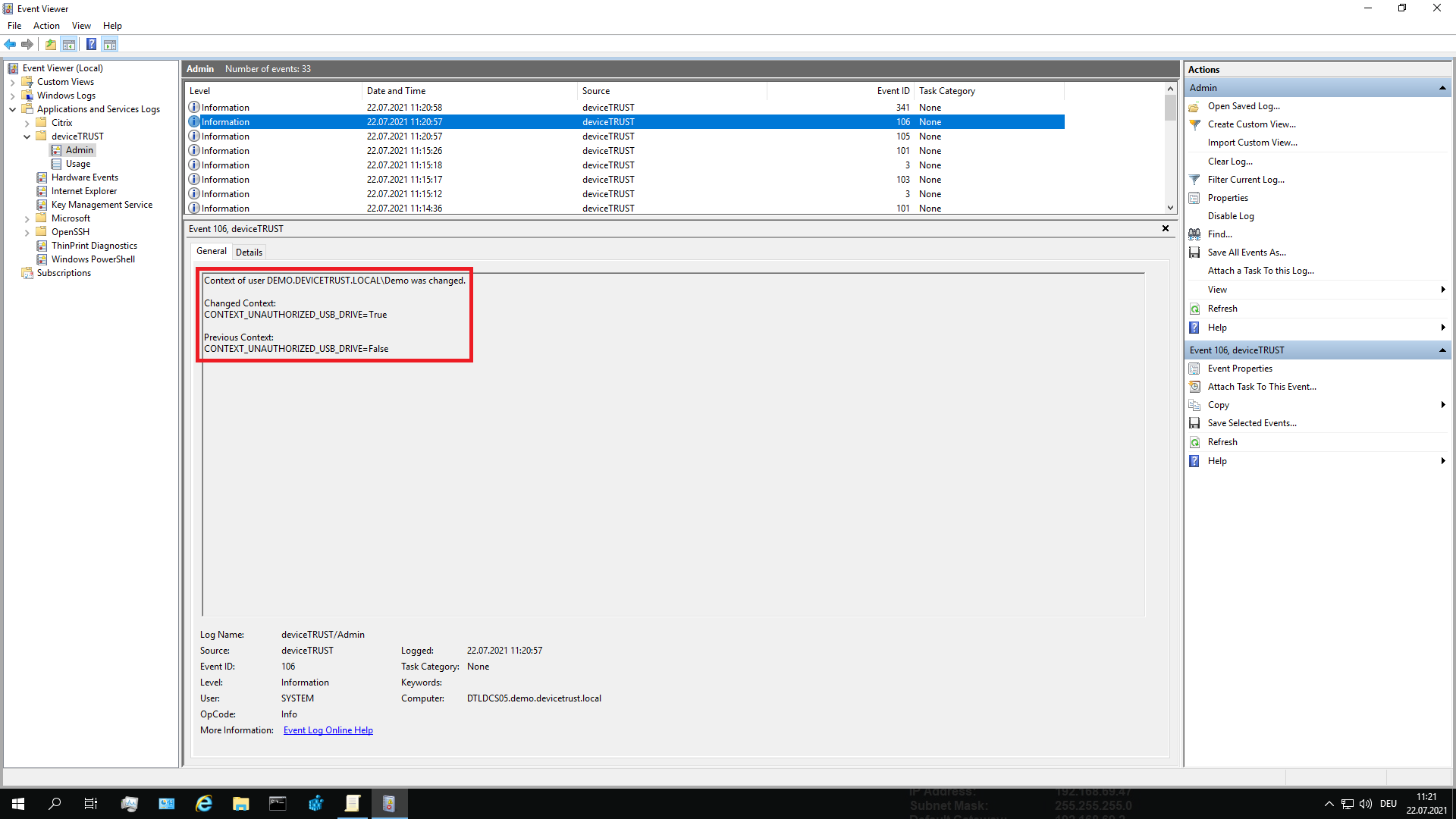
In the above example, we can force a context change on the local device by plugging in an unauthorized USB drive and see how the corresponding context is updated. To check this, open the Windows Event Log on the local device and navigate to APPLICATION AND SERVICE LOGS\DEVICETRUST\ADMIN and check for Event ID 106, which is raised whenever a context changes value within the users’ local session.
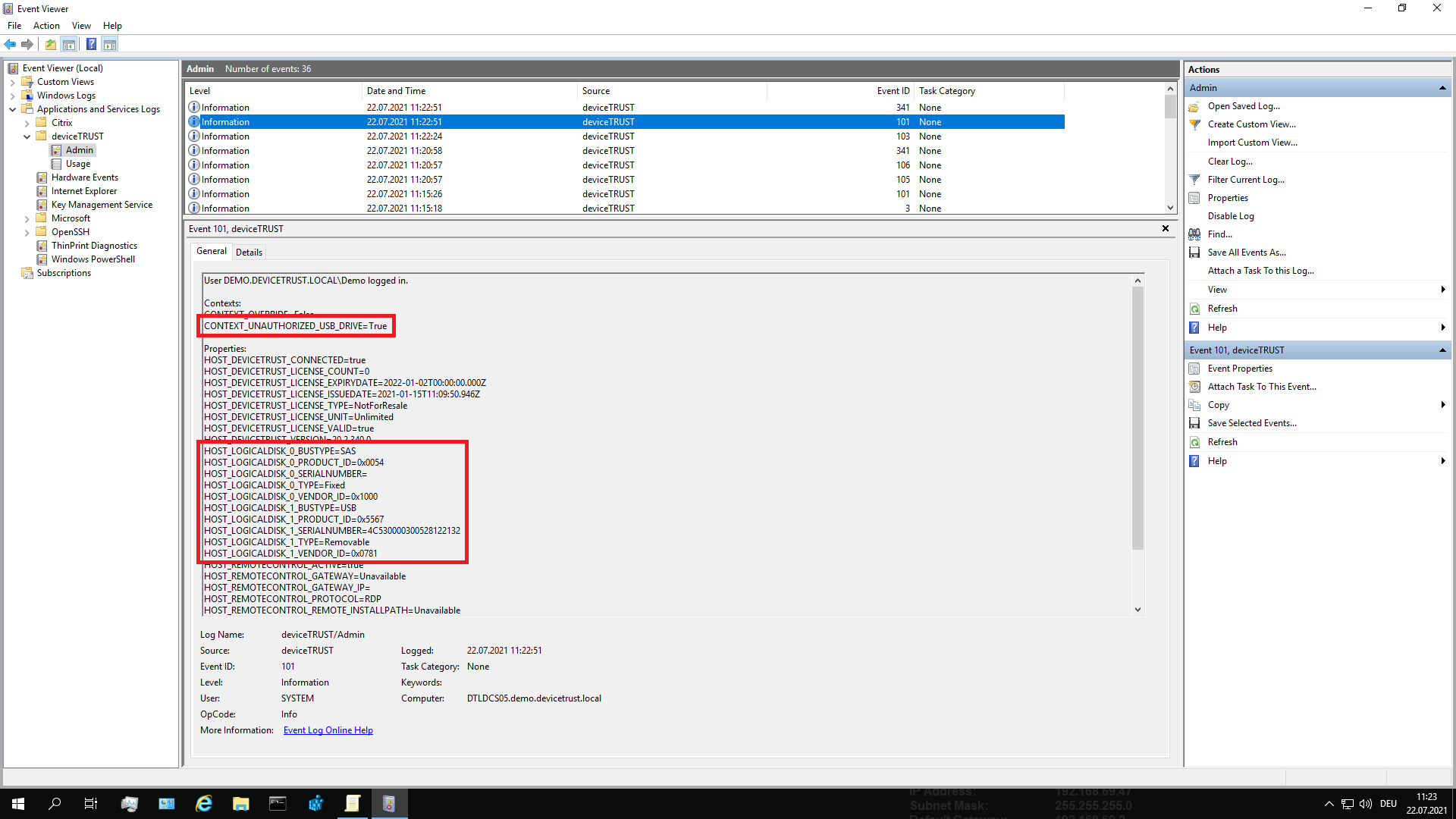
If the context takes the correct value, the logic for the context definition is correct. If this is not the case, the individual properties used within the context definition should also be checked. Check within your context definition which properties are used for the logic and check the accuracy of the logic based on the submitted properties and adjust them if necessary. To do this, open the Windows Event Log on the local device and navigate to APPLICATION AND SERVICE LOGS\DEVICETRUST\ADMIN and check for Event ID 101, which details the properties and context of the users’ local session.
Step 5: Exclude specific users from the deviceTRUST policy
It may be necessary to exclude a user or user group from the deviceTRUST contextual security policy, for example, to quickly grant access independently of deviceTRUST on a local device.
To exclude a user, open your active deviceTRUST contextual security policy and navigate to DEVICETRUST CONSOLE and click on the SETTINGS tab. Select LICENSING, navigate to the USERS tab and add the user or the user group to the UNMANAGED USERS to exclude them completely from deviceTRUST.
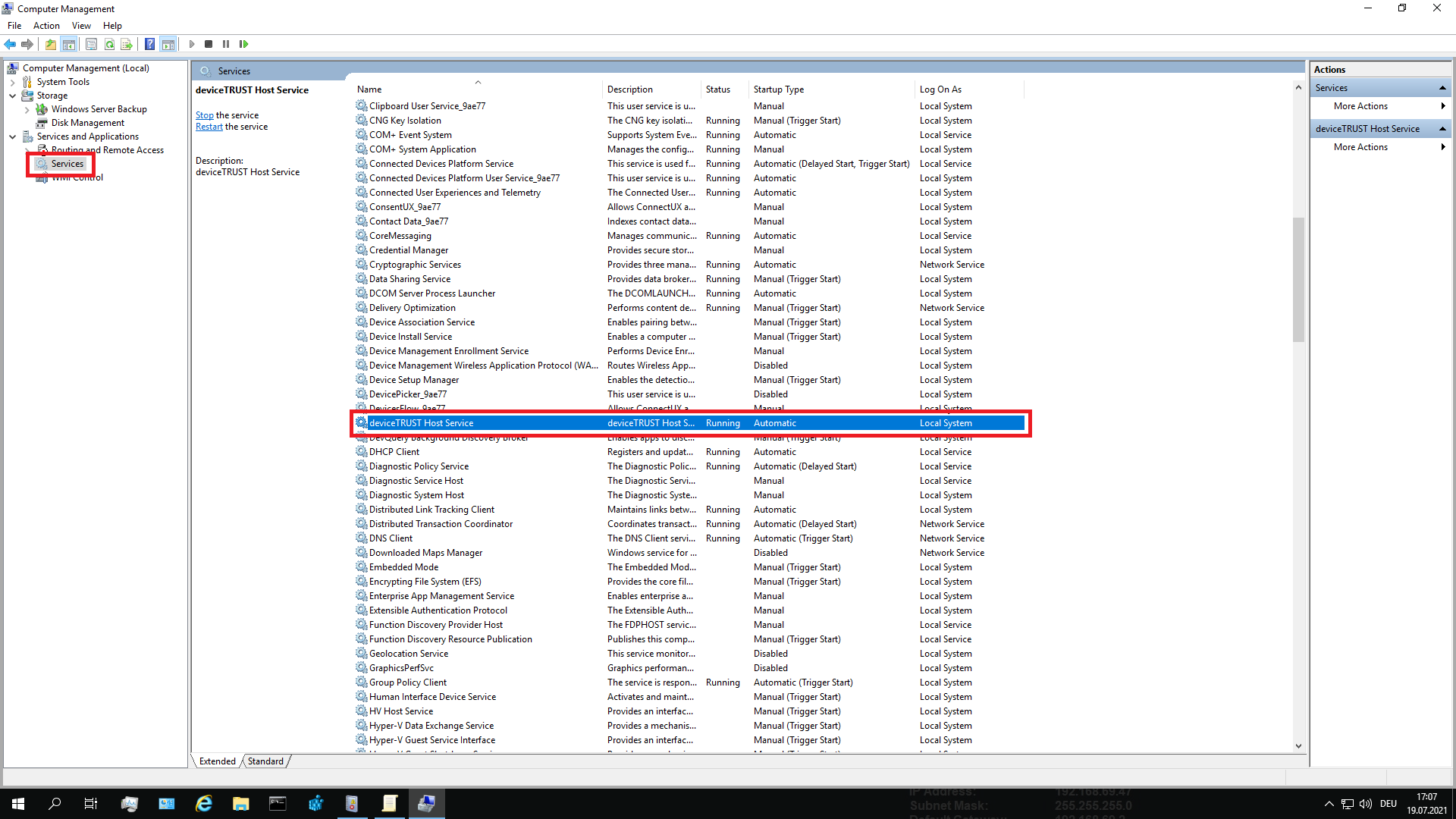
Step 6: Check that the deviceTRUST Host service is running
The deviceTRUST Host service must be running on the local device for it to enforce the policy. If this service is not running, then no deviceTRUST contextual security policies can be applied to the users. The deviceTRUST Host service is monitored by standard operating system functions and recovered if necessary.
Open the COMPUTER MANAGEMENT on the local device, navigate to SERVICES AND APPLICATIONS, select SERVICES and check that the DEVICETRUST HOST SERVICE is running. If the service is not running, try to start it from the menu or context menu by selecting START.
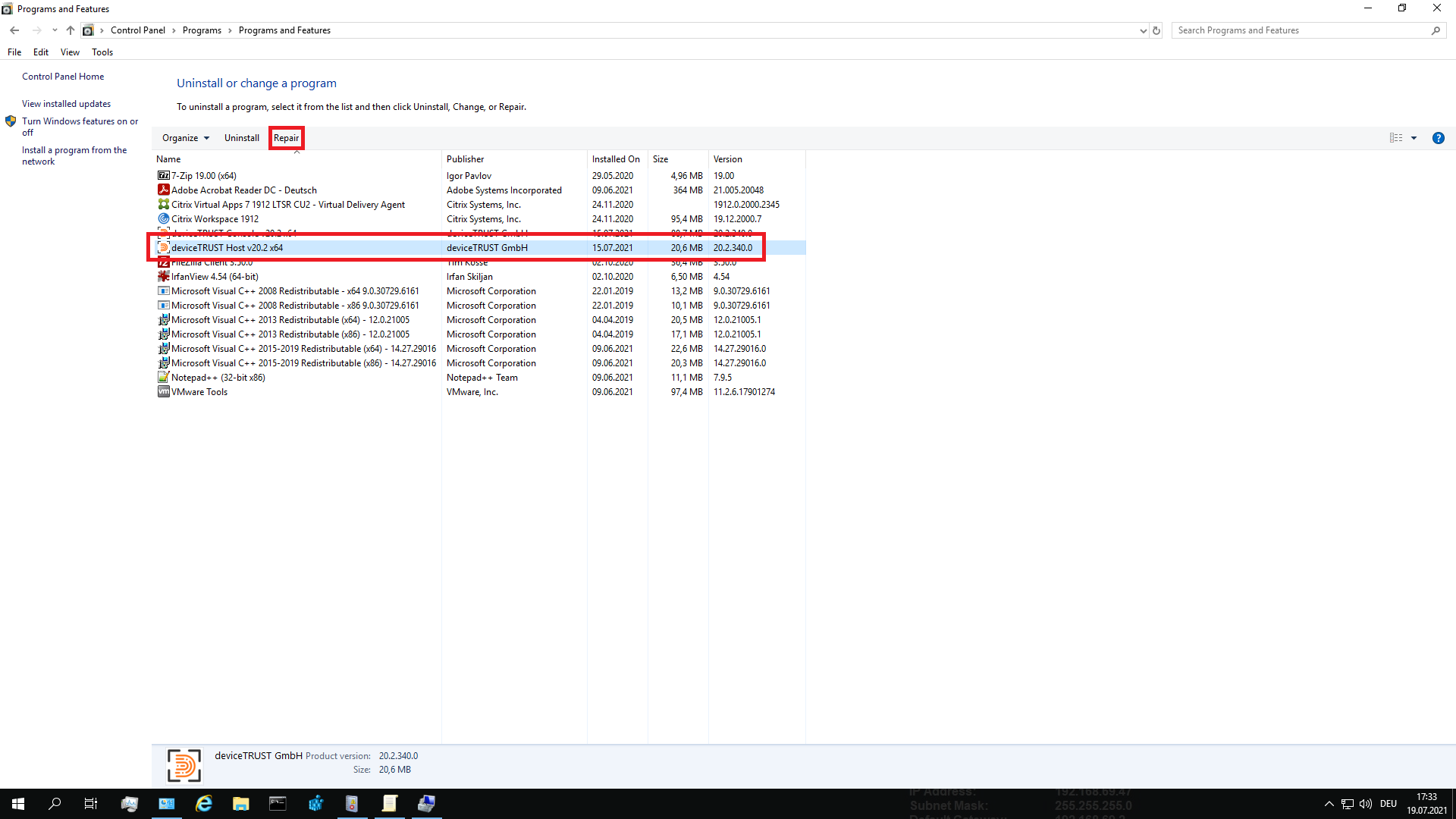
If the deviceTRUST Host service does not start you can repair the deviceTRUST Host installation. To do this, please open the CONTROL PANEL, navigate to PROGRAMS and open PROGRAMS AND FEATURES. Select DEVICETRUST HOST VXX.X X64 and start the repair of the installation with the REPAIR button.
Step 7: Check that you are using the latest deviceTRUST version
The latest deviceTRUST releases may contain bugfixes that were present in previous releases, or compatibility fixes that have since been discovered with other third party components. Therefore, it is recommended to upgrade to the latest deviceTRUST version from time to time. This can be done very easily by transparently updating the corresponding deviceTRUST component (Host and Console) by running the newer installer.
The following points should be considered before upgrading:
- Before you start the upgrade, read the release notes for all releases since the version you have currently deployed.
- The deviceTRUST Host and the deviceTRUST Console must always be on the same version.
The latest deviceTRUST software can be found on our Download page.
Step 8: Open a support ticket with us
If none of the steps in the troubleshooting guide helped, or if you have any further questions, feel free to open an appropriate ticket via our support contact form.
